TZ’s financial inclusion index hits 0.81 in 2024
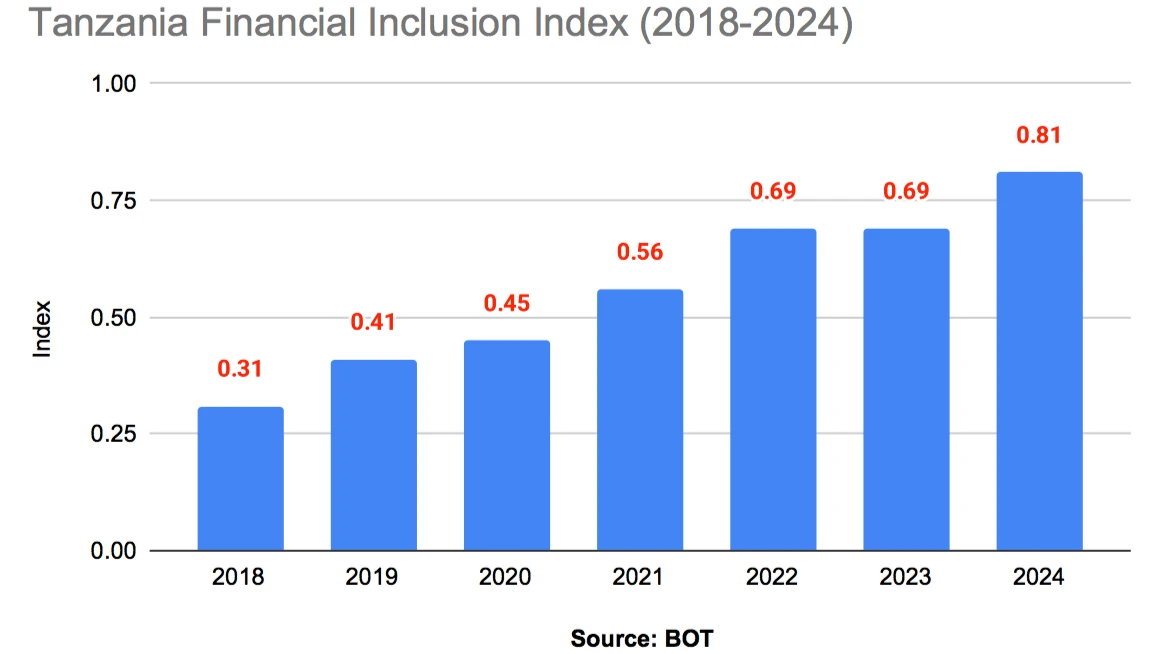
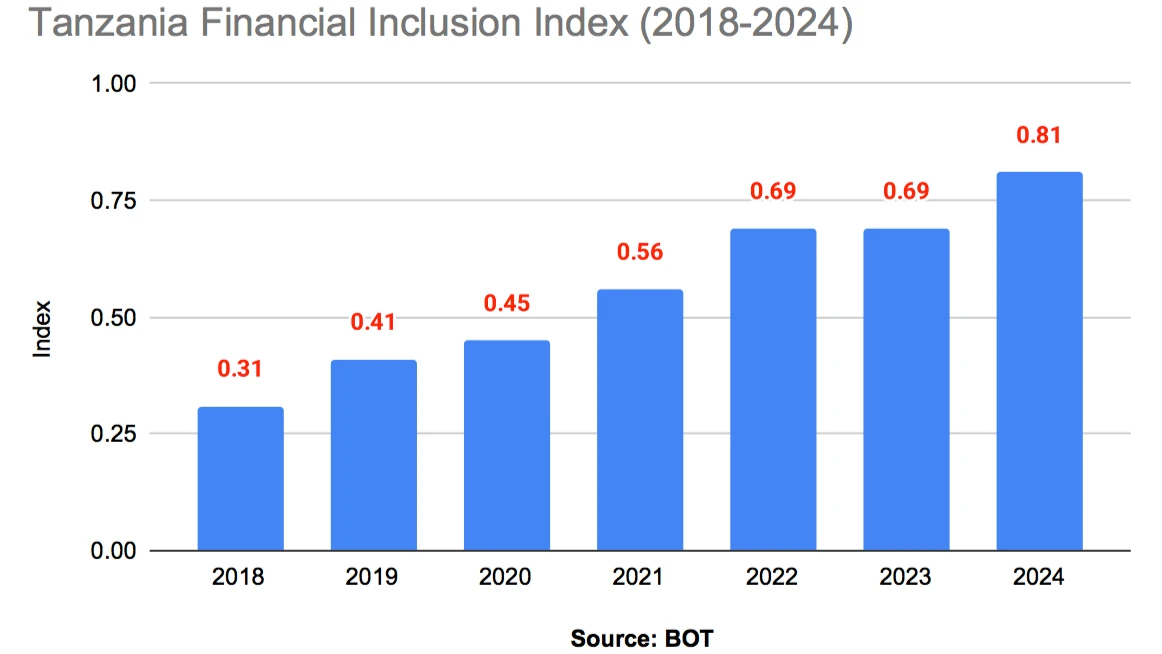
Tanzania’s Financial Inclusion Index (TanFiX) rose to 0.81 in 2024 from 0.69 in 2023, driven mainly by the expansion of digital financial services and stronger consumer protection measures, the Bank of Tanzania (BoT) has said.
According to BoT’s 2024 Annual Financial Inclusion Report, digital financial services significantly enhanced convenience, accessibility, and affordability for Tanzanians. An index of 0.81 means Tanzania has achieved about 81 percent of the ideal state of financial inclusion.
TanFiX, a key barometer of access to and use of financial services, tracks changes in financial inclusion indicators per 100,000 adults over time. According to the report, access dimension sub-index, which measures the availability and proximity of financial services, improved to 0.83 in 2024 from 0.76 recorded in 2023, mainly driven by an increase in mobile money and bank agents, microfinance tier II services providers and community microfinance groups.
Usage dimension sub-index which measures the frequency and activeness of individuals and businesses in using financial services, increased to 0.78 in 2024 from 0.75 recorded in the previous year, mainly associated with the increase in number of loan accounts in microfinance tier II and digital loans.
In 2024, the report notes, Digital Financial Services (DFS) remained vital in providing individuals and businesses with access to financial services, improving financial management, and fostering participation in the digital economy.
“Regulatory reforms, such as the FinTech Regulatory Sandbox and enhanced consumer protection frameworks, have strengthened trust, transparency, and market integrity,” said BoT Governor Emmanuel Tutuba.
The central bank says it received 14 applications for sandbox testing, which are under review.
Similarly, the Tanzania Insurance Regulatory Authority (TIRA) has prepared draft regulations and a concept paper to establish Insurance Regulatory Sandboxes.
In July 2024, the Tanzania Bankers Association (TBA) also held a virtual session on cloud computing, advocating for pro-technology regulatory frameworks to support wider use of innovations such as cloud computing in the banking sector.
“While we celebrate these milestones, we remain aware of persistent challenges, particularly in deepening usage and improving service quality. Addressing these will require sustained innovation, targeted policies, and strengthened partnerships to build a resilient and inclusive financial ecosystem,” Tutuba added.
The report highlights progress in expanding access, usage, quality, and innovation in financial services, with special attention to women, youth, micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs), smallholder farmers, fishers, and persons with disabilities.
Key gains include an 18.97 percent increase in mobile money agents to 1.48 million, and a 23.5 percent rise in telecom subscriptions to 86.8 million. More than 21 million National IDs were registered, supporting improved interoperability of identification systems. Electricity access reached 52.3 percent of rural hamlets, while financial literacy programs benefited over 27,000 rural residents.
Digital financial services also expanded sharply. Active mobile money accounts rose by 17.5 percent to 60.75 million, while digital loan accounts doubled to 193 million—61.9 percent of them owned by women. Gross premiums in digital insurance services reached 1.4trn/-.
During the year, BoT advanced research on Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), while financial institutions rolled out new products targeting underserved groups, particularly MSMEs and women. The number of mobile money agents grew by 235,229 to 1,475,281 by December 2024.
The report also noted ongoing initiatives by financial institutions and Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) to promote inclusion through digital innovation, public awareness, and financial literacy programs.
MNOs improved network availability in underserved areas such as Arusha, Babati, Geita, Kagera, Iringa, Lindi, Mara, Tabora, and Ruvuma.
Meanwhile, the Savings and Credit Cooperative Union League of Tanzania (SCCULT) conducted sensitization workshops and helped establish 10 Savings and Credit Cooperative Societies (SACCOS) in Tanga and Kagera regions.
In addition, following the 2023 FinScope Survey, which highlighted areas with low levels of financial inclusion, stakeholders launched targeted initiatives in Singida and Lindi to address barriers to affordable and high-quality financial products and services.
Top Headlines
© 2025 IPPMEDIA.COM. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED